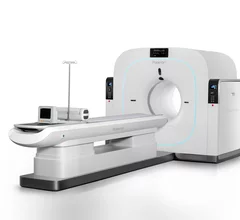
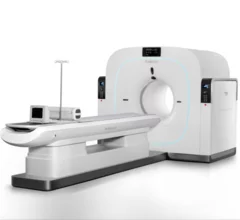
Nuclear Cardiology
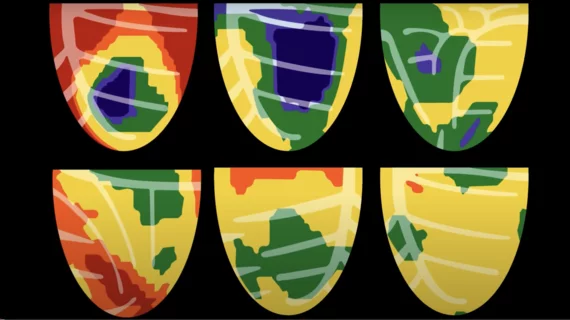
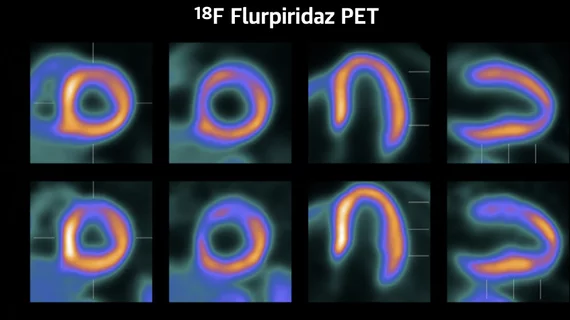
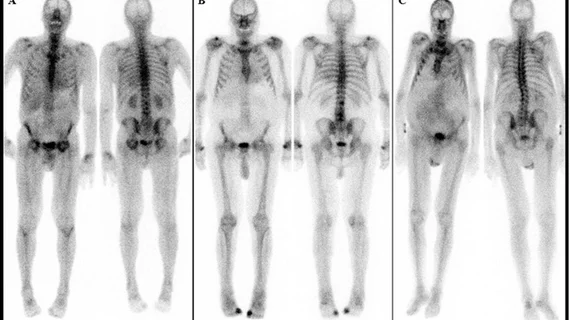
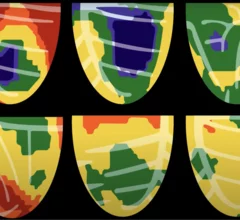
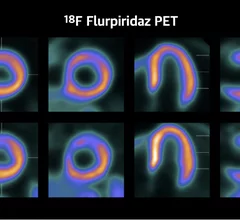
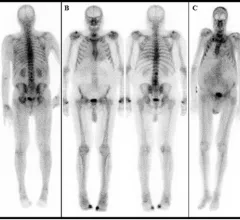
Single photon computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) molecular imaging are used as primary cardiac imaging modalities to evaluate the function of the heart. It uses radioactive isotopes attached to sugars that are metabolized by cardiomyocytes. This creates an image of the metabolic activity of the heart and shows areas of ischemia or infarct. Other radiotracers can image the heart to diagnosis cardiac amyloidosis and sarcoidosis.
Displaying 1 - 8 of 103