CVIS
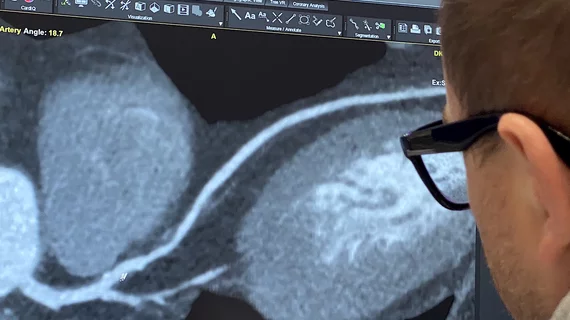
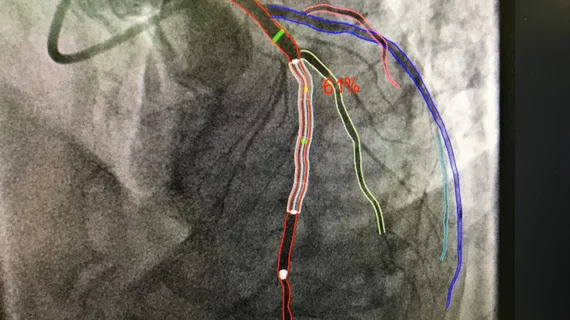
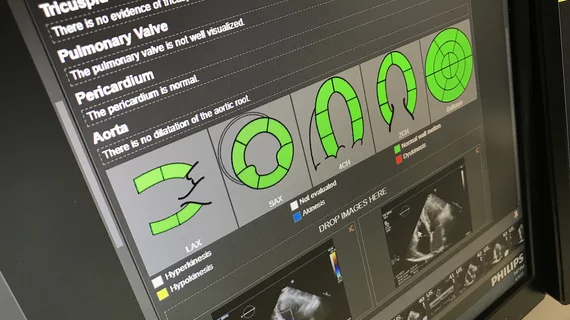
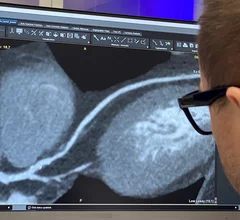
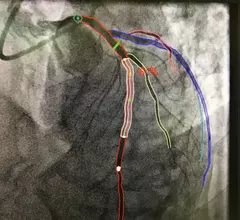
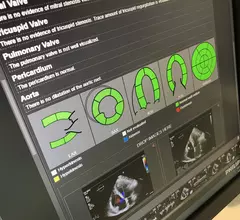
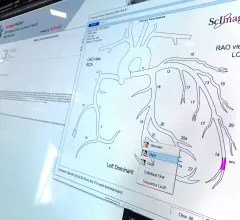
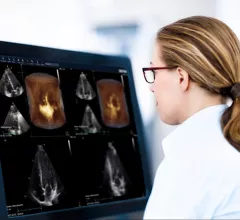
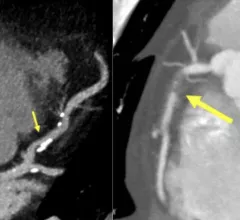
Cardiovascular information systems (CVIS) include electronic reporting systems for all aspects of the cardiovascular service line. These health informatics systems often incorporate cardiac PACS and reporting systems for echocardiography, cath lab, cardiac surgery, electrophysiology (EP), ECG and diagnostic testing. Today, these systems are often web-enabled or web-based and integrated tightly with a healthcare system's electronic medical record (EMR).
Displaying 1 - 8 of 49