Electrocardiography
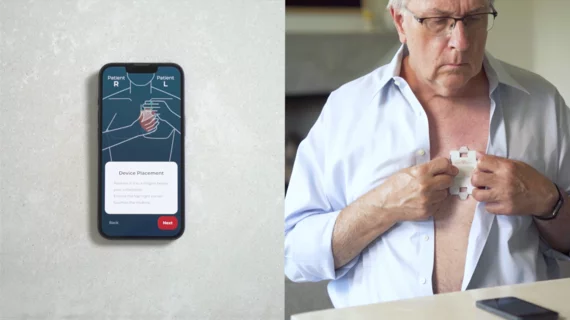
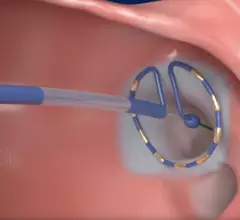
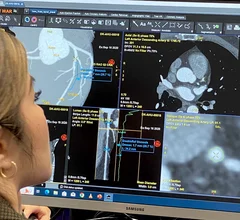
Electrocardiograms (ECG) are a primary cardiac diagnostic test that measures the electrical activity in heart to identify overall cardiac function, arrhythmias and areas of ischemia and infarct. Standard 12-lead ECG breaks the 3D structure of the heart into 12 zones, each showing the electrical activity in that specific area of the heart. This narrows down areas where there are issues with coronary artery disease or electrophysiology issues. Many ambulatory heart monitors and consumer-grade ECG monitors use fewer leads so are less specific as to cardiac conditions or location of abnormal heart rhythms, but can show an issue that requires further diagnostic testing or treatment.



![A majority of medical devices involved in Class I recalls were never required by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to undergo premarket or postmarket clinical testing, according to new research published in Annals of Internal Medicine.[1]](/sites/default/files/styles/240x220/public/2024-09/istock-1209664264.jpg.webp?itok=OEoT1RAi)