Cardiac PET
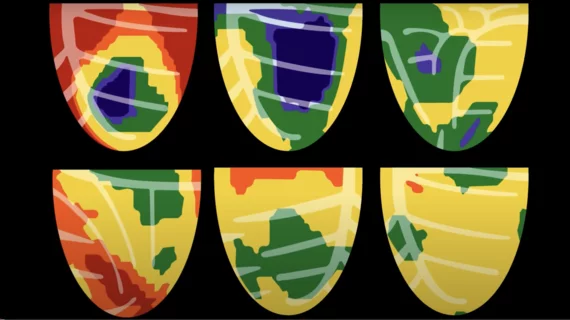
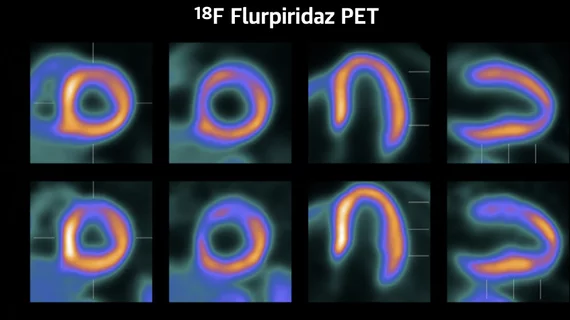
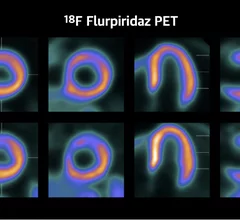
Cardiac positron emission tomography (PET) is a nuclear imaging modality that can show heart cell metabolism that reveals areas of ischemia or infarct where this low or no blood flow due to coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction. PET can help determine in if areas of the heart effected by a heart attack can be reversed through revascularization. PET can also offer additional information on the patient's condition with myocardial flow reserve (MFR) information. Cardiac PET uses a rubidium (Rb-82) radiotracer injection, which only has a half life of 75 seconds, which greatly speeds scan times compared to traditional cardiac SPECT imaging.