Acute Coronary Syndromes
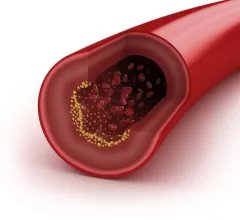
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is most commonly caused by a heart attack (myocardial infarction) where blood flow to the heart is suddenly blocked. This is usually caused by a blood clot from a ruptured coronary artery atherosclerotic plaque. Other causes include spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD), which most commonly occurs in women. ACS is usually treated in a cath lab with angioplasty and the placement of a stent to prop the vessel open.
Displaying 665 - 672 of 694