Structural Heart Disease
Structural heart diseases include any issues preventing normal cardiovascular function due to damage or alteration to the anatomical components of the heart. This is caused by aging, advanced atherosclerosis, calcification, tissue degeneration, congenital heart defects and heart failure. The most commonly treated areas are the heart valves, in particular the mitral and aortic valves. These can be replaced through open heart surgery or using cath lab-based transcatheter valves or repairs to eliminate regurgitation due to faulty valve leaflets. This includes transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). Other common procedures include left atrial appendage (LAA) occlusion and closing congenital holes in the heart, such as PFO and ASD. A growing area includes transcatheter mitral repair or replacement and transcatheter tricuspid valve repair and replacement.
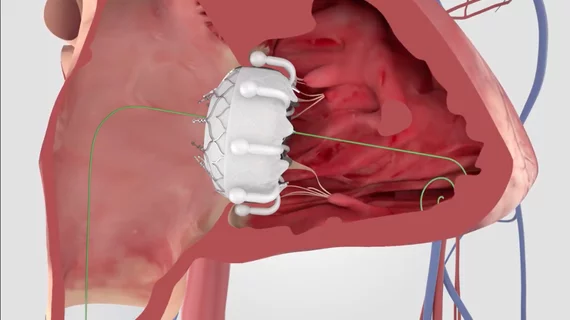

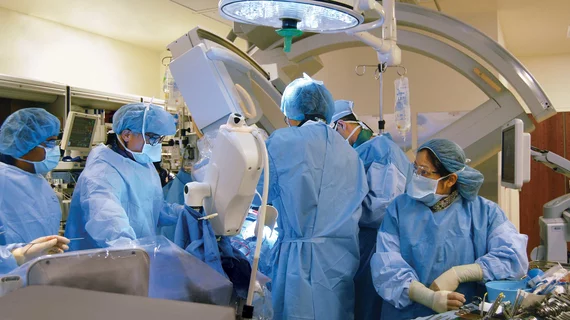
![Back in October 2024, heart surgeons with the WVU Heart and Vascular Institute in Morgantown, West Virginia, performed the world’s first robotic aortic valve replacement and coronary artery bypass (RAVCAB) procedure. Now, the team behind that historic surgery has shared its full story for the first time, publishing an in-depth look at the procedure in The Annals of Thoracic Surgery, an official journal from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons.[1]](/sites/default/files/styles/top_stories/public/2024-12/screenshot_2024-12-11_at_2.09.27_pm.png.webp?itok=7GogEebJ)