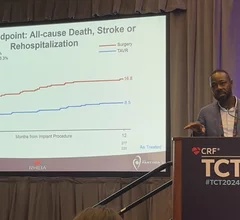
TAVR
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is a key structural heart procedure that has rapidly expanded in the decade since it was first FDA cleared. TAVR has come a paradigm shift in how many aortic stenosis patients are treated, now making up more than 50% of U.S. aortic valve replacements. It is less invasive than open heart surgery and recovery times are greatly reduced. TAVR can also be used in patients who otherwise are too high risk to undergo surgery. TAVR is referred to as transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) in many placed outside of the U.S. TAVR inspired the growing areas of transcatheter mitral repair or replacement and transcatheter tricuspid valve repair and replacement.
Displaying 33 - 40 of 443
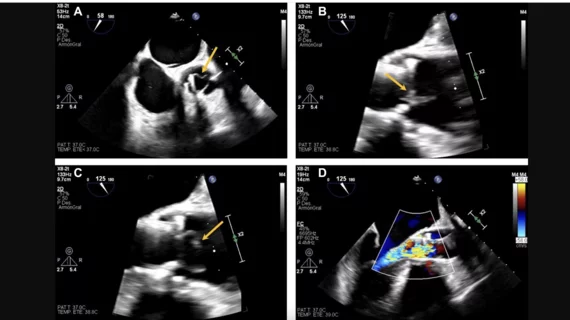

![A majority of medical devices involved in Class I recalls were never required by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to undergo premarket or postmarket clinical testing, according to new research published in Annals of Internal Medicine.[1]](/sites/default/files/styles/top_stories/public/2024-09/istock-1209664264.jpg.webp?itok=gQInU1vO)