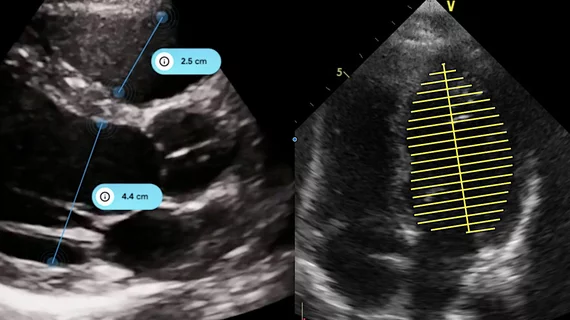
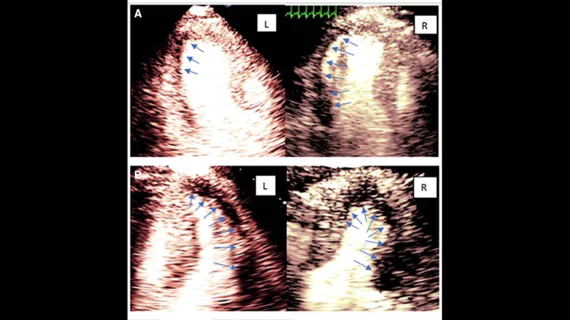
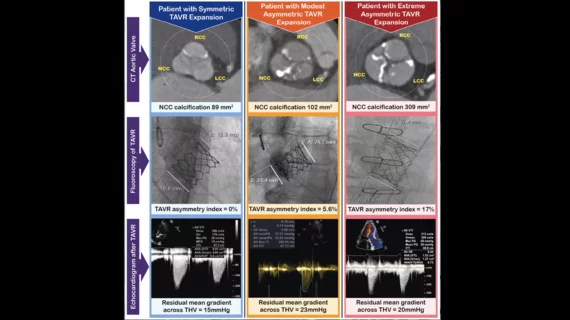
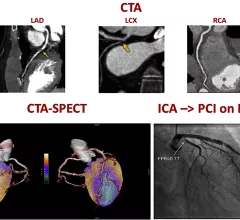
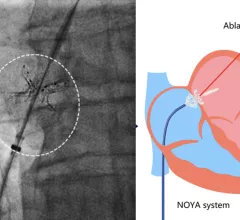
Echocardiography
Cardiac ultrasound uses reflected sound waves (echos) to create images of anatomy inside the body. Echocardiograms are the primary cardiac imaging modality used to assess the heart and diagnose or track cardiac issues. Echo is the gold standard imaging modality to assess the heart, particularly with calculating left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), which is a measure of cardiac output. In addition to noninvasive standard transthoracic echo (TTE), invasive transesophgeal echo (TEE) is also used when clearer, more detailed imaging of the heart is needed. Both 3D and 4D echo echo systems are rapidly gaining wider adoption and enable new types of assessments, especially in the structural heart space and in transcatheter procedural guidance. Find news on general ultrasound imaging.